We set up Dovecot with virtual mailboxes and LDAP-based authentication. Now, we turn our attention to Postfix, the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) responsible for routing outgoing and incoming emails. We will configure Postfix for multi-domain email, so that our one VM handles domain1.com, domain2.com etc.
Moreover, we set it up as a relay using AWS SES for outgoing messages. Without SES, most servers like gmail.com will reject our messages by default.
Postfix can easily integrate with Dovecot for delivery and authentication, and with LDAP for dynamically routing email across multiple virtual domains like domain1.com and domain2.com.
Postfix:
- Receives mail via SMTP or Submission
- Looks up valid recipients using LDAP
- Hands off messages to Dovecot via LMTP
- Relays outbound mail through a provider like AWS SES
1. Install Postfix
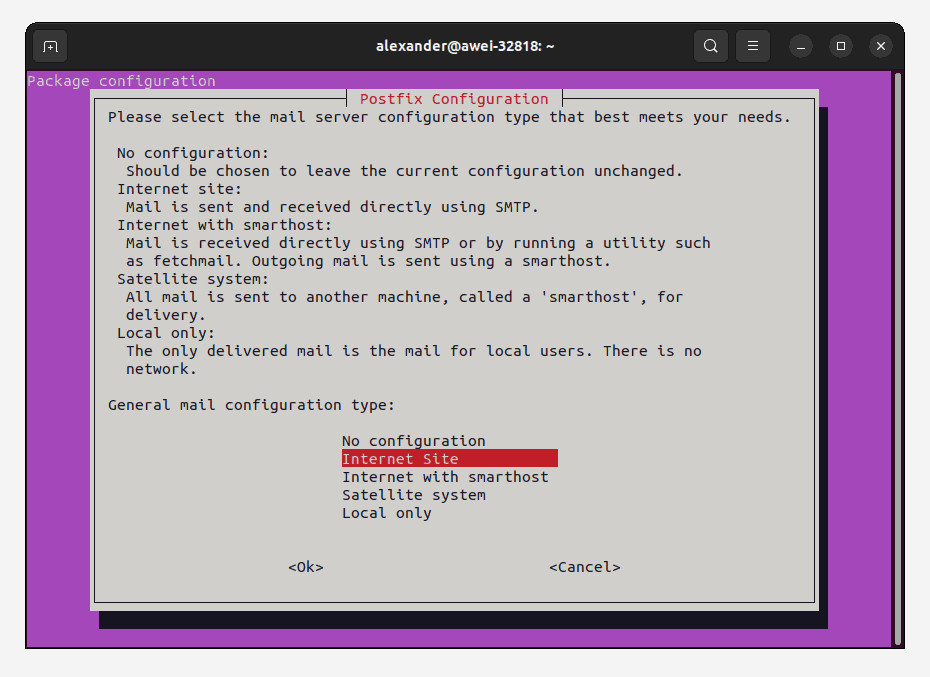
sudo apt install postfix postfix-ldap libsasl2-modulesDuring installation, choose:
- “Internet Site”
- System mail name:
mail.domain1.com
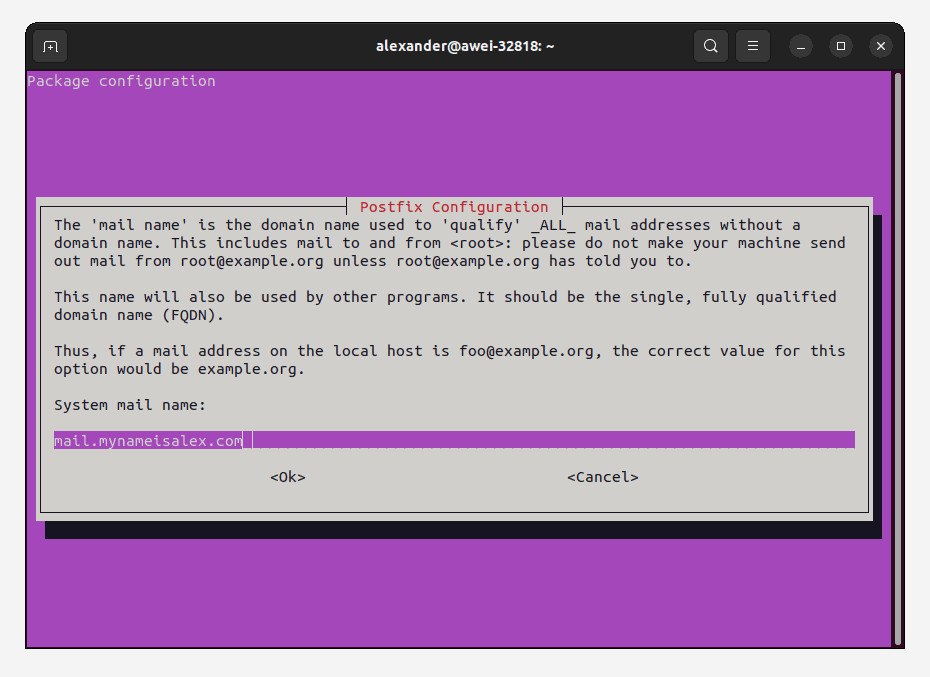
Pick any one of your virtual domains that you configured with LDAP for the system mail name, and obtain a corresponding SSL certificate.
2. Virtual Domain Delivery via LDAP
Define Virtual Domains
In /etc/postfix/main.cf:
virtual_mailbox_domains = ldap:/etc/postfix/ldap-domains.cf
virtual_alias_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/virtual_aliases
virtual_mailbox_maps = ldap:/etc/postfix/ldap-users.cf
virtual_transport = lmtp:unix:private/dovecot-lmtpThis tells Postfix:
- Which domains are accepted (
ldap-domains.cf) - Which user mailboxes exist (
ldap-users.cf) - How to deliver mail to them (via Dovecots LMTP socket)
Define Alias File
/etc/postfix/virtual_aliases:
@domain1.com user1@domain1.com
@domain2.com user2@domain2.com
@domain3.com user3@domain3.comThen run:
postmap /etc/postfix/virtual_aliasesThis acts as a domain-level catch-all, rerouting any address at those domains to specific inboxes.
3. Configure LDAP for Postfix Multi-Domain Email
To allow Postfix (and Dovecot) to perform LDAP lookups, we create a limited-permission service account called dovecot-reader. This user binds to the LDAP directory and searches for email addresses and domain mappings:
dn: cn=dovecot-reader,dc=mail
objectClass: simpleSecurityObject
objectClass: organizationalRole
cn: dovecot-reader
Update the bind_dn and bind_pw fields in your LDAP config files to match this user (and remember to make them owned by root:root and have permissions 0640).
/etc/postfix/ldap-domains.cf
server_host = 127.0.0.1
search_base = dc=mail
query_filter = (|(dc=%s)(associatedDomain=%s))
result_attribute = dc
version = 3
bind = yes
bind_dn = cn=dovecot-reader,dc=mail
bind_pw = YOUR_PASSWORD/etc/postfix/ldap-users.cf
server_host = 127.0.0.1
search_base = dc=mail
query_filter = (mail=%s)
result_attribute = mail
version = 3
bind = yes
bind_dn = cn=dovecot-reader,dc=mail
bind_pw = YOUR_PASSWORD4. Enable SMTP Auth (SASL)
SMTP authentication lets users securely send email through the server. For security and spam prevention, we configure Postfix to only allow mail submission from authenticated users.
This happens over the Submission port (587), which is distinct from port 25 used for server-to-server transfers.
In /etc/postfix/main.cf:
smtpd_sasl_type = dovecot
smtpd_sasl_path = private/auth
smtpd_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtpd_tls_auth_only = yes
smtpd_tls_security_level = may
smtpd_recipient_restrictions =
permit_mynetworks,
permit_sasl_authenticated,
reject_unauth_destinationIn /etc/postfix/master.cf:
submission inet n - y - - smtpd
-o syslog_name=postfix/submission
-o smtpd_tls_security_level=may
-o smtpd_tls_auth_only=no
-o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes
-o smtpd_sasl_type=dovecot
-o smtpd_sasl_path=private/auth
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,rejectThe submission service listens on port 587 and is used by email clients (like Thunderbird, iPhone Mail, or PHPMailer) to send messages through your mail server.
Unlike port 25, which is primarily used for server-to-server delivery, the submission port enforces authentication, ensuring only authorized users can send messages. With
-o smtpd_tls_security_level=mayTLS is optional (so that localhost services like Roundcube webmail can authenticate using plaintext), but this can be made a hard requirement.
5. Enable TLS
Ensure:
smtpd_tls_cert_file = /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.domain1.com/fullchain.pem
smtpd_tls_key_file = /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.domain1.com/privkey.pemYou can test with:
openssl s_client -connect mail.domain1.com:587 -starttls smtp6. Outbound Relay (Postfix Multi-Domain Email Server)
To use AWS SES,
In /etc/postfix/main.cf:
relayhost = [email-smtp.us-east-2.amazonaws.com]:587
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
smtp_sasl_security_options = noanonymous
smtp_tls_security_level = encryptCreate /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd:
[email-smtp.us-east-2.amazonaws.com]:587 SMTP_USERNAME:SMTP_PASSWORDThen:
postmap /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
sudo systemctl restart postfix7. Verify LDAP Lookups
postmap -q alex@domain1.com ldap:/etc/postfix/ldap-users.cfExpected: alex@domain1.com
Postfix is now ready to:
- Accept email for multiple domains
- Use LDAP to verify users and domains
- Deliver mail to Dovecot via LMTP
- Authenticate clients with SASL over TLS
- Relay outbound messages securely via AWS